The Week in COVID & Schools: CDC Data Shows Access to In-Person Learning Varied By Race and Region, Where Colleges Are (and Aren’t) Requiring Vaccinations & More

This is our weekly briefing on how the pandemic is shaping schools and education policy, vetted, as always, by AEI Visiting Fellow John Bailey. Click here to see the full archive. Get this weekly roundup, as well as rolling daily updates, delivered straight to your inbox — sign up for The 74 Newsletter.
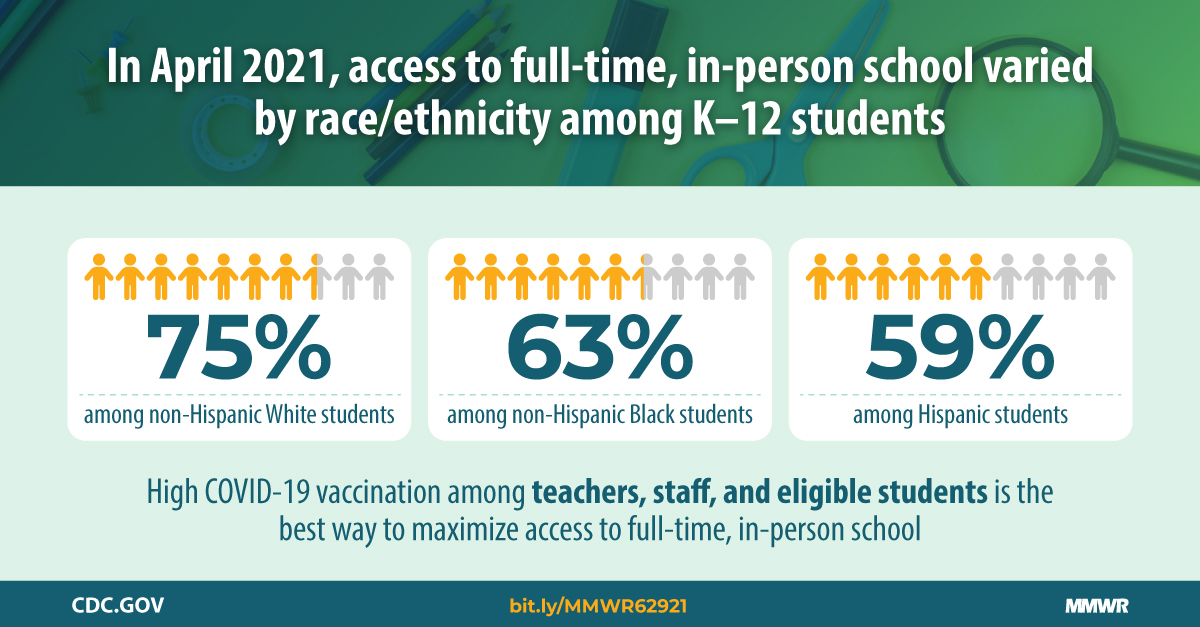
Disparities in Learning by Region and Race: New report from the CDC:
- “Reduced access to in-person learning is associated with poorer learning outcomes and adverse mental health and behavioral effects in children.”
- “Disparities in full-time in-person learning by race/ethnicity existed across school levels and by geographic region and state. These disparities underscore the importance of prioritizing equitable access to this learning mode for the 2021-22 school year.”
- Massive differences in different parts of the country. More students (including students of color) were in-person in the South than in the West and Northeast.
- See the state-by-state data here.
- Really good visualization from The Philadelphia Inquirer.
July 9, 2021 — The Big Three
COVID-19 and Schools — The Evidence for Reopening Safely: Via Nature
- “A growing body of evidence suggests that schools can be opened safely. But that hasn’t quelled debate over whether they should be open and, if so, what steps should be taken to limit the spread of the virus.”
- “Equity also became a flashpoint in the debate. Researchers argued that remote learning would widen disparities between white students and students of color in many countries.”
- “One of the largest studies on COVID-19 in schools in the United States looked at more than 90,000 pupils and teachers in North Carolina over nine weeks last autumn. Given the rate of transmission in the community, ‘we would have expected to see about 900 cases’ in the schools, says Daniel Benjamin, a pediatrician at Duke Clinical Research Institute in Durham, North Carolina, and co-lead author on the study. But when the researchers conducted contact tracing to identify school-related transmissions, they identified only 32 cases.”
- “The bulk of the literature on transmission in schools … suggests that kids aren’t driving viral spread. Investigations in Germany, France, Ireland, Australia, Singapore and the United States show no, or very low, secondary attack rates within school settings.”

Vaccine Mandates at Colleges: A Washington Post report shows the percentage of two- and four-year colleges and universities that are requiring students to be vaccinated against the coronavirus.
- “More than 500 colleges and universities plan to require coronavirus vaccination for at least some of their students and employees, according to data as of Tuesday from the Chronicle of Higher Education.”
Texas state test results reveal dramatic drop in the number of students on grade level: Nearly 4 in 10 failed math tests.
- “In districts where fewer than a quarter of classes were held in person, the number of students who met math test expectations dropped by 32 percentage points, and the number of students who met reading expectations dropped by 9 percentage points compared to 2019, the last time the test was administered.”
- “In districts with more than three-quarters in-person instruction, the number of students meeting math expectations only dropped by 9 percentage points and those who met reading expectations by 1 percentage point. Students of color and lower-income students saw greater gaps as well, although those gaps were smaller than the one between remote and in-person instruction.”
- “Math test performance saw the most significant drop, from 50 percent of students meeting their grade level in 2019 to only 35 percent this year.”
- “This is probably 800,000 more students in Texas in mathematics that are noticeably below grade level this year as a result of COVID than in normal years,” Education Commissioner Mike Morath said. “It is important to remember that these are not numbers. These are children.”
Federal Updates
Infrastructure deal: The bipartisan 58 member Problem Solvers Caucus endorses the bipartisan infrastructure plan.
- A Punchbowl News survey of senior Capitol Hill staffers finds that 40 percent say that only a “hard” infrastructure bill will pass, and the American Families Plan and the full American Jobs Plan will be left by the wayside.
- “The White House’s long sought-after bipartisan infrastructure deal could hit the Senate floor as early as the week of July 19,” Politico reports.
Education Department:
- Approved state American Rescue Plan Elementary and Secondary School Emergency Relief plans for South Dakota, Texas, Massachusetts, Utah, Arkansas, Rhode Island and Washington D.C.
- Is inviting states to complete the application for their share of the second disbursement of $800 million in funds for homeless youth.
- Announced new appointees:
- Katy Neas, deputy assistant secretary, Office of Special Education and Rehabilitative Services
- Toby Merrill, deputy general counsel, Office of the General Counsel
- Hayley Matz Meadvin, senior adviser, Office of the Secretary
- Chris Soto, senior adviser, Office of the Secretary
- Antoinette Flores, senior adviser for American Rescue Plan implementation, Office of Postsecondary Education
- Deven Comen, chief of staff, Office of Communications and Outreach
- Abel McDaniels, special assistant, Office of Elementary and Secondary Education
Emergency Connectivity Fund: The Federal Communications Commission officially opened the application window for schools and libraries to file applications for the $7.17 billion fund aimed at closing the homework gap. Education Superhighway has guides, resources and webinars on the program.
National Center for Education Statistics: Total K-12 enrollment dropped by roughly 3 percent in 2020-21 compared with the previous school year. More via The 74.
City & State News
Illinois: The Chicago Teachers Union released a proposal for reopening schools. The union is asking for:
- 80 percent of students 12 and older to be vaccinated against COVID-19 by October and 80 percent of younger students within 60 days after FDA emergency use authorization for their age group.
- Ventilation system upgrades at school buildings.
- A 10 percent increase in special education teachers, bilingual teachers, English language program teachers, teacher assistants and arts educators by Jan. 27 to support community recovery.
- The union also wants members who are medically unable to return in-person to fill positions at the district’s new remote-learning Virtual Academy for students with qualifying health conditions.
Florida: Full-time enrollment in Florida Virtual School was up between July and September by 5,644 – a 98 percent increase – while the flexible virtual program saw course requests increase by 231,128, or 57 percent, from the same time in 2019.
Maryland: Maryland schools should drop all mask mandates, writes Margery Smelkinson, an immunology and infectious-disease scientist.
Michigan: Health department releases new mask and physical distance recommendations for schools which mostly points to CDC guidance.
New Jersey: The pandemic set back student learning. Newark kept the data under wraps. “Nearly 80 percent of third-graders and almost 90 percent of fourth-graders would ‘not meet the passing score’ on the state math exams, according to a district analysis that was not made public,” Chalkbeat reports.
COVID-19 Research
Delta Variant:
- In Los Angeles County, the pace of Delta’s spread has prompted officials to reinstate mask guidance for public indoor spaces — regardless of vaccination status.
- In the UK, 375,000 students were absent due to Delta cases at the end of June — the highest number since children returned to school in March. That number jumped to 640,000 last week.
Damage to Children’s Education — and Their Health — Could Last a Lifetime: Via Kaiser Health News. Long, but worth reading the whole piece.
Masks Can Prevent COVID-19 Transmission in Schools: New study from Duke (and an interview): “Proper masking is the most effective mitigation strategy to prevent secondary transmission in schools when COVID-19 is circulating and when vaccination is unavailable, or there is insufficient uptake.”
Doctors Are Puzzled by Heart Inflammation in the Young and Vaccinated: Via Katherine Wu in The Atlantic.
- “These events are, so far, not matching the most terrifying versions of the condition, which have been observed with coronavirus infections.”
- “Rather, compared with more typical cases of myocarditis, the ones linked to the vaccines, on average, involve briefer symptoms and speedier recoveries, even with less invasive treatments. Still, the incidents are showing up in the few days that follow each vaccine’s second dose at higher-than-expected rates, especially in boys and young men, and no one is yet sure why.”
- “All of these factors make the risk of this complication tough to quantify, and several researchers have criticized the CDC’s recent evaluation. But most of the experts I spoke with said that the calculations still come out strongly in favor of vaccination, in part because of another set of disconcerting ambiguities, this time on the side of the virus.”
What Parents With Unvaccinated Kids Need to Know About the Delta Variant This Summer: Via The Wall Street Journal
Vaccinating Teens: To fully vaccinate children against COVID-19 by the time school starts, many parents must act now, CNN reports.
- “It takes five weeks to be fully vaccinated with Pfizer’s vaccine, the only one authorized for adolescents ages 12 to 17. That means, for example, Atlanta students need to get their first shot by July 1 to be fully immunized by the first day of school on Aug. 5.”
Viewpoints
How COVID-19 is Inspiring Education Reform: Via The Economist
- “Big shocks have sometimes changed schooling for the better. The Second World War midwifed the Butler Act in Britain, which increased years of compulsory schooling and abolished the fees still charged by many state schools. After Hurricane Katrina inundated New Orleans, officials there embarked on sweeping school reforms. Nine years later graduation rates had increased by 9-13 percentage points.”
- “Struggling learners would benefit enormously if expanded tutoring schemes become core parts of education systems. A long-running tutoring programme at Match Charter Public School in Boston provides one model. Before the pandemic it offered all children in four grades daily tutoring in maths. It operates a longer school day than is common in its neighbourhood, so Match manages to slot these sessions into students’ timetables without them having to give up anything else.”
Make Telemedicine Services for Children Permanent: Kelly Wolfe, a former educator and advocacy leader for children’s health in Minnesota and vice president of strategic partnerships and regulatory compliance at PresenceLearning, writes at The 74: During COVID, states let students get speech therapy, mental health counseling and other services online. Make those changes permanent.
Survey of Black Parents: From Morning Consult/EdChoice
- Black parents remain less likely than white and Hispanic parents to vaccinate themselves or their children.
- Roughly half of Black parents believe it will be safe to send children back to school for in-person classes by September. But 31 percent said it will take longer.
- Read the brief and the crosstabs.
How the Pandemic Helped Fuel the Private School Choice Movement: Via EdWeek:
- “Six states had enacted new programs by July 1, and a bill to create a new program in Missouri awaited Gov. Mike Parson’s signature. Governors also approved expansions of 14 existing voucher and tax-credit scholarship programs by loosening eligibility restrictions or expanding their budgets.”
- “Among the biggest moves in states’ 2021 legislative sessions: West Virginia created the most-expansive education savings account program in the country, making most of the state’s students eligible for the Hope Scholarship Program, which will provide up to $4,600 in state funds per student. New Hampshire’s budget includes a new educational savings account program available to families with incomes up to 300 percent of the federal poverty line.”
The Pandemic Will Worsen Illiteracy. Another Outcome Is Possible: Via Emily Freitag in EdWeek.
Some Students Thrived Learning From Home — They Deserve a Permanent Model: Via Javaid Siddiqi
#TurnThePageProject: The Walton Family Foundation and COVID Collaborative launched a digital project that includes unique perspectives from parents, practitioners and thought leaders on what they believe the future of learning looks like.
- The project includes Common, Drew Furedi, Eddie Koen, Elmo, Emily Oster, Jessica Hamilton, Kaya Henderson, Maria Hinojosa, Mikala Streeter, Nekima Levy Armstrong, Shalinee Sharma, Sharon McMahon, Tim Shriver, Tom Frieden, Viridiana Carrizales, Zahir Mbengue and Ze Min Xiao.
…And on a Lighter Note
This Dad: Has his hands full.
ICYMI @The74
Weekend Reads: In case you missed them, our top five stories of the week:
- Critical Race Theory: Chaos Theory — Amid Pandemic Recovery Efforts, School Leaders Fear Critical Race Furor Will ‘Paralyze’ Teachers
- Student Health: Spread of Delta Variant Marks ‘Most Dangerous’ Time in Pandemic for Kids, May Force Schools to Re-Up Safety Measures, Experts Say
- Looking Ahead: 12 Big Challenges From Last School Year That Could Now Define the Fall of 2021 — From Learning Loss to Restoring Trust, Closing Achievement Gaps & More
- Pandemic Recovery: Analysis: Most Students in Urban Districts Will Have Summer Learning Options, But Schools’ Plans May Miss the Mark
- Federal Data: Almost All Schools Offered In-Person Learning by Spring, But Attendance Varied Widely By Race
Disclosure: John Bailey is an adviser to the Walton Family Foundation, which provides financial support to The 74.
Get stories like these delivered straight to your inbox. Sign up for The 74 Newsletter

;)